Gaining weight is something that many of us worry about as we age. You may attribute the weight gain to a slowed metabolism rate due to ageing. However, a recent study conducted in 2021 has shown that our metabolism rate remains rather consistent from age 20 to 60[1]. So, what is the real reason behind the “slowed metabolism rate”? Poor diet, lack of physical activity, hormonal changes, and stress are some of the factors contributing to weight gain[2]. Studies have revealed that women in their 30s are particularly susceptible to weight gain[3]. Moreover, losing weight becomes more challenging at this age due to the progressive decline of growth[4]. For most women, the typical areas of weight gain are the hips, arms, and thighs, while others may experience it in the abdomen and chest.
As women age, there are several reasons why they may experience weight gain:
1. Poor diet and lack of physical activity
The main reason for most weight gain is due to our diet and sedentary lifestyle. As we spend more time sitting down and have less time for physical activity, our daily calorie expenditure decreases. The remaining unused energy is then stored as fats, as fats are the most efficient source of energy (1 gram of fat supplies the body with about 9 calories, twice as much as that of protein and carbohydrates)[5]. On top of that, our diet these days often consists of high amounts of saturated fats and sugar, exceeding the recommended daily intake of 1800 calories for women.
In TCM, weight gain is attributed to the accumulation of Dampness in the body. Dampness is usually formed as a result of poor circulation or a poor digestive system that fails to regulate the flow of nutrients and water in the body.
2. Hormonal changes
As we age, some hormone levels in our body decrease, and two key hormones that influence weight gain are growth hormone and estrogen. Growth hormone is responsible for reducing and redistributing body fat. Decreased levels of growth hormone have been linked to obesity, particularly in individuals with abdominal fats[6].
On the other hand, estrogen, known as the female hormone, plays a role in fat metabolism. It can increase the level of high-density lipoprotein (HDL or “good” cholesterol) while decreasing the level of low-density lipoprotein (LDL or “bad” cholesterol)[7]. However, as women reach their late 40s to 50s, estrogen levels decline due to the ovaries producing lesser amounts. This hormonal decrease leads to an imbalance in the proportion of HDL and LDL, resulting in a higher deposition of cholesterol in the body.
Moreover, estrogen positively affects insulin sensitivity. With lower levels of estrogen, insulin resistance increases, leading to higher levels of glucose in the bloodstream. Cells then convert this glucose to fat for long-term storage, contributing to weight gain[8].
3. Sleep deprivation
Sleep is essential for our body to rest, repair, and rejuvenate so that we have sufficient energy to carry out tasks the next day. However, we often fail to get the recommended 8 hours of sleep daily[9], leading to feeling fatigued and low on energy. Research shows that sleep duration influences the levels of ghrelin (hunger hormone) and leptin (satiety hormone) in our body. Shorter sleep duration increases ghrelin and decreases leptin, making us more prone to feeling hungry and consuming more calories[10]. If you tend to sleep late, you might find yourself craving snacks at night as a result. This could also make it harder to lose weight.
4. Stress
Stress is something that we cannot avoid in modern society. There has been a correlation between the amount of stress and obesity[11]. Obesity is usually seen in people with high stress. Cortisol (stress hormone) will increase when stress levels increase. This will lead to an increase in appetite and also increased fat accumulation in the stomach.
What are the health risks of weight gain?

Complications of weight gain can include the following: increased risk of high blood pressure, high cholesterol, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and musculoskeletal disorders. A study has shown that there is evidence that higher amounts of body fat is associated with an increased risk of certain cancers, noticeably endometrial and postmenopausal breast cancer for women[12].
Obesity is accompanied with a chronic state of low level inflammation that is brought about by metabolic cells in response to excess nutrients in the body[13]. Obesity will also activate the inflammatory responses of immune cells that are abundant in adipose tissue. This will in turn lead to inflammation and impairment of the immune system, which explains the increased risk of chronic conditions and cancer[14].
TCM tips to prevent weight gain in women
i. Dietary adjustment
Lifestyle adjustments play a critical role in weight management. Start by making dietary changes such as reducing the consumption of oily, fried, and sweet foods and drinks. TCM theory suggests that frequent consumption of greasy and fried foods can strain the Spleen and Stomach, leading to their deficiency and poor digestion. This can contribute to Dampness accumulation in the body, ultimately leading to weight gain.
ii. Exercise and weight management
Moving towards a healthy weight through regular exercise is a key factor in controlling weight gain. Engaging in 150 minutes of moderate to vigorous exercise per week can create an anti-inflammatory environment in your body and support a healthy gut[15]. Beyond weight management, exercise also reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease[16], promoting overall well-being.
iii. Sleep well and manage your mental well-being

Getting sufficient good quality sleep and maintaining your mood can help you maintain a healthy weight. If you struggle with sleep issues, consider trying Sleep Essentials, a TCM supplement enhanced with the latest sleep-aid ingredients specially formulated to improve sleep and boost mood. The TCM herb Semen Ziziphi Spinosae (Suan Zao Ren) in Sleep Essentials nourishes Liver Yin and reduces Heart Fire, rebalancing Yin and Yang to address the root cause of insomnia. Additionally, Sleep Essentials contains 5-HTP, which can be converted into serotonin (a happy chemical) and melatonin (a sleep hormone), supporting improved mood and better sleep.
In-clinic treatments and therapies to help with weight management
i. Wellness Assessments

Left to right: Biowell Meridian Scan, Heart Rate Variability (HRV) Assessment and Thermography Body Heat Map
To help us understand your body better and optimise your treatment plans, we use 3 tech-enhanced wellness assessments to get insights on your body condition:
1. Biowell Meridian Scan uses gas discharge visualisation technology to analyse your meridian energy level and identify imbalances in your body. Usually for obesity issues, the scan is likely to show imbalances in the Spleen and Stomach. Insights from this scan is used to support our physicians in their diagnosis and prescriptions that typically aims to boost the body’s energy levels so that it functions optimally.
2. Heart Rate Variability (HRV) Assessment measures the time interval between heartbeats to determine the stress levels and the body’s capability to adapt to external changes. For weight management cases, HRV assessment allows the physician to track the stress levels over the course of treatment and change the treatment accordingly to help the patient manage stress.
3. Thermography Body Heat Map maps body temperature to identify areas with inflammation and poor blood circulation. With the help of the thermography body heat map, we can identify if the cause of the weight gain is largely due to poor circulation in the body.
The process for the wellness assessments are quick and non-invasive. With the help of the wellness assessments, our physicians will be able to come up with treatment plans better suited to your conditions.
ii. Acupuncture
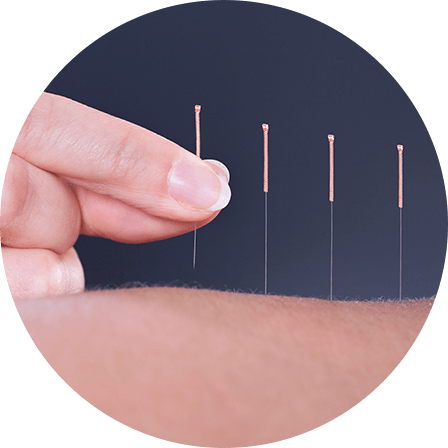
To help with the prevention of weight gain and weight loss, acupuncture can be used to promote body metabolism and eliminate Dampness by stimulating the acupoints along the Spleen and Stomach meridians. Acupuncture can also improve sleep by stimulating acupoints on the head or along the Heart meridian. To relieve stress and soothe the mood, acupoints along the Liver meridians can be used.
iii. Electro-Lymphatic Therapy (ELT)
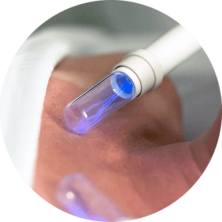
Electro-Lymphatic Therapy is an FDA registered wellness device to stimulate better lymphatic drainage and flow. With better lymphatic drainage, inflammation in the body can be cleared effectively, promoting better circulation to remove the Dampness in the body as well.
Your healing is the most important!
At Oriental Remedies Group, most of our physicians are trained in both Biomedical Science and TCM at Nanyang Technological University (Singapore) and China for a minimum of 5-8 years before being certified to practise in Singapore. If you or your loved one is suffering from weight management issues and seeking a way to manage the condition, consult our physicians at +65 8087 0486 for a targeted treatment plan.
—–
This article is written by Physician Yap Chong Sin (Oriental Remedies Group, Singapore), a registered TCM physician certified by the Traditional Chinese Medicine Practitioners Board (TCMPB).

Note: All words in Italics refer to the TCM organ-system and not the anatomical organ referenced in western medicine.
Disclaimer:
The content on this page is for information and educational purposes only. Such medical information may relate to disease, injury, drugs and other treatments, medical devices and/or health products. Medical information does not amount to advice, and if advice is needed an appropriate professional help should be sought. The disclaimer asserts that no warranties or representations are given in respect of the medical information, and that the website operator should not be held liable if a user suffers any injury or loss after relying upon the medical information.
All wellness assessments and technology-enhanced therapies using wellness device(s) are intended for use only for general well-being purposes or to encourage or maintain a healthy lifestyle, and it is not intended to be used for any medical purposes (such as detection, diagnosis, monitoring, management or treatment of any medical condition or disease). Any health-related information provided by these devices should not be treated as a medical advice. Please consult a physician for any medical advice required.
References:
[1]: https://www.sma.org.sg/smj/4505/4505a1.pdf
[2]: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/obr.13002
[3]: https://cfps.org.sg/publications/the-singapore-family-physician/article/71_pdf
[4]: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279163/
[6]: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8300043/
[7]: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1731455/
[8]: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6341301
[9]: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21368739/
[10]: https://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.0010062
[11]: https://www.nature.com/articles/0803229
[12]: https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMsr1606602
[13]: https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/pdf/10.1146/annurev-immunol-031210-101322
[14]: https://joe.bioscientifica.com/view/journals/joe/222/3/R113.xml
[15]: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41569-018-0065-1
[16]: https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01970.x

