Male sexual dysfunction refers to any disturbance of sexual function that prevents individuals or their partner from enjoying sexual activity and constitute conditions such as erectile dysfunction, also known as impotence (with the latter term less commonly used now), premature ejaculation, low libido, delayed orgasm/ejaculation.
With the topic of sexual dysfunction remaining taboo, men find it hard to open up and seek professional help. In this article, we discuss male sexual dysfunction in-depth, treatments available as well as top tips to alleviate sexual dysfunction. We hope to change your perspective, sexual dysfunction is just like any other health condition out there.
Sexual dysfunction is more common than you think!

*Study on Erectile dysfunction [1]; Study on Premature ejaculation [2]
While sexual dysfunction commonly affects older men (age 45 and above), it is a condition that can affect adult men of all ages, especially in our generation. The 2 most common forms of sexual dysfunction affecting men are Erectile dysfunction (ED) and Premature ejaculation (PE). [3]
Who is more likely to experience male sexual dysfunction?
| Factors | How it affects your male sexual functions |
| Age
While older males (above 45) are more likely to be affected, sexual dysfunction can affect men of all ages, especially in our sedentary generation. |
Ageing, chronic health conditions and poor lifestyle habits are associated with poorer vascular and nerve health, which have a direct impact on men’s sexual functions. Low testosterone levels in men affect libido and erection. |
| Chronic health conditions
e.g. high blood pressure, diabetes, heart disease, high cholesterol, low testosterone, nerve-related disease, obesity |
|
| Poor lifestyle habits
Smoking, sedentary lifestyle, excessive alcohol consumption, excessive weight gain |
|
| Psychological issues
e.g. stress, low confidence, sexual anxiety, depression, relationship problems |
As sexual activity (e.g. desire for sexual intimacy, erection, orgasm, ejaculation) is largely controlled by our nervous system, any form of psychological issues could affect the sexual response. |
Why is it important to seek help early?
On the emotional side of things, proper sexual function is important in any relationship. Having a healthy sex life strengthens your bond and emotional intimacy with your partner.
Leaving sexual dysfunction unattended could spiral into a vicious cycle where stress, sexual anxiety and relationship problems worsen your sexual dysfunction.
In addition, sexual function problems can be an early warning of other chronic conditions. Recent research concluded, erectile dysfunction might be an indicator of poor cardiovascular health. [4]
Can you fully recover from sexual dysfunction?
With the right cause identified, doctors and TCM physicians can work out a treatment plan that includes lifestyle and dietary changes to improve your condition. In other words, with the right treatments, the chances of recovering or getting your sexual dysfunction managed are very high. The earlier you seek treatment, the easier it is to manage the condition.
“We’re living in a time where information is readily available and help is everywhere. This makes it so much more important to seek treatment from trusted professionals that you are comfortable with.”
~ Dr. Chan Jun Yang
What are the main types of sexual dysfunction in men?
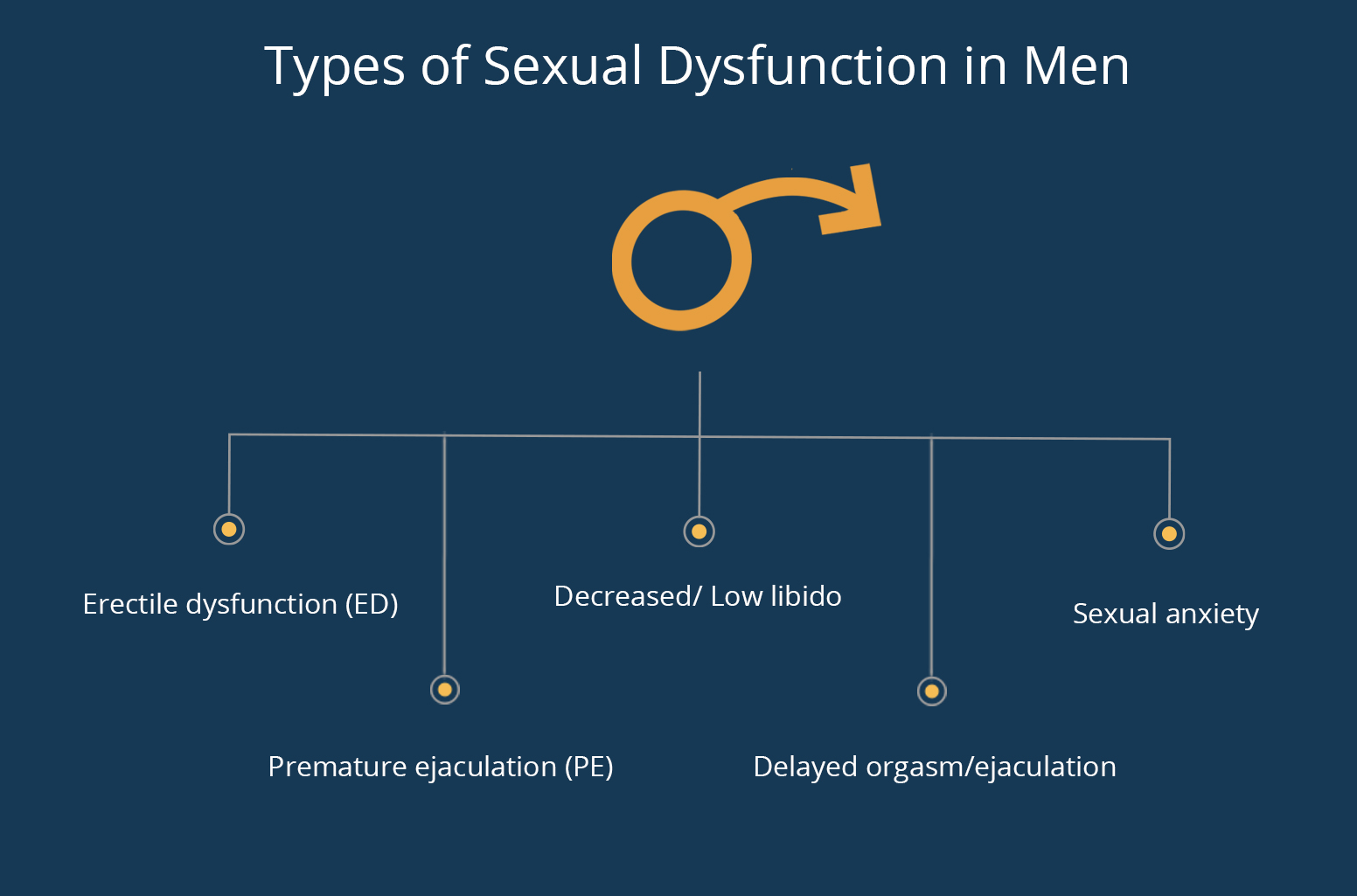
1. Erectile dysfunction (ED) (阳痿)
It is the repeated inability to achieve or maintain an erection for satisfactory sexual performance.
What causes it:
-
- Psychological issues (e.g. relationship issues, depression, anxiety, stress, worrying about ED, fatigue)
- Ageing
- Poor lifestyle (e.g. excessive alcohol intake, lack of exercise, smoking, obesity)
- Chronic health problems (high blood pressure, high cholesterol, heart disease, diabetes, nerve disease)
- Hormonal disorders (e.g. low testosterone)
- Medications (e.g. antidepressants, certain blood pressure medications)
- Liver Qi stagnation syndrome
- Blood-stasis syndrome
- MingMen Fire weakening syndrome
- Heart-Spleen deficiency syndrome
- Yin deficiency raging Fire syndrome
- Phlegm-Damp syndrome
2. Premature ejaculation (PE) (早泄)
It is early or rapid ejaculation that happens before the male and his partner would like.
What causes it:
-
- Psychological issues (e.g. relationship issues, depression, anxiety, stress, fatigue)
- Low levels of brain neurotransmitters
i.e. serotonin - Testosterone deficiency
- Prostate problems (e.g. infection, inflammation)
- Concurrent ED (males with ED may form a habit of rushing to ejaculate as they are worried of the inability to maintain the erection)
- Liver Qi stagnation syndrome
- MingMen Fire weakening syndrome
- Heart-Spleen deficiency syndrome
- Yin deficiency raging Fire syndrome
3. Decreased/ Low libido (性欲减退)
It is the lack of sexual desire or sex drive to put it simply.
What causes it:
-
- Often linked to stress, relationship issues, low self-esteem, and fatigue
- Medical conditions (e.g. testosterone deficiency)
- Sexual dysfunctions such as ED and PE
- Liver Qi stagnation syndrome
- MingMen Fire weakening syndrome
- Heart-Spleen deficiency syndrome
- Phlegm-Damp syndrome
4. Delayed orgasm/ejaculation
It is a persistent difficulty or delay in attaining orgasm after sufficient sexual stimulation, causing emotional distress.
What causes it:
-
- Psychological issues (e.g. relationship issues, depression, anxiety, stress)
- Reduced penile stimulation due to frequent or unusual masturbation techniques, hyperstimulation (e.g. porn), disparity between fantasy and partner
- Ageing
- Medications/substances (e.g. antidepressants, excessive alcohol use)
- Health conditions (e.g.diabetes, nerve disease, low testosterone)
- Prostate surgery
5. Sexual anxiety (性焦虑)
Also known as sexual performance anxiety typically results from negative thoughts about your ability to perform well.
What causes it:
-
- Fear of not being able to satisfy partner sexually
- Self-esteem issues like body weight, body image
- Problems in your relationship
- Concern about premature ejaculation or taking too long to reach orgasm
- Anxiety about not being able to have an orgasm or enjoy the sexual experience
- Liver Qi stagnation syndrome
- Phlegm-Damp syndrome
Sexual dysfunction from a TCM perspective
In TCM, imbalances and disharmony in the body lead to the development of health conditions and sexual dysfunction is one of them. The 6 most common syndromes causing sexual dysfunctions are:
- MingMen Fire weakening syndrome (命门火衰证)
- Liver Qi stagnation syndrome (肝郁气滞证)
- Phlegm-Damp syndrome (痰湿阻滞证)
- Yin deficiency raging Fire syndrome (阴虚火旺证)
- Heart-Spleen deficiency syndrome (心脾两虚证)
- Blood-stasis syndrome (血脉瘀滞证)
1. MingMen Fire weakening syndrome (命门火衰证)
Mingmen is an area between the second and third lumbar vertebra. In TCM, our reproductive function and potency is directly linked to the MingMen. Poor MingMen Fire can arise from hereditary conditions, excessive sexual activity and old age. When the Fire is weak or diminished, the quality of the Kidney Qi will likewise be reduced, causing erectile dysfunction, low libido and even premature ejaculation.
2. Liver Qi stagnation syndrome (肝郁气滞证)
TCM believes that the Liver is in charge of regulating emotions. Stress and negative emotions cause fluctuation in your emotions. Over time this wears out the Qi in the Liver meridian, causing Liver Qi stagnation syndrome.
As the Liver meridian is directly linked to the penis, Qi stagnation at the Liver will lead to poor erectile function,premature ejaculation, low libido and in severe cases, sexual anxiety.
3. Phlegm-Damp syndrome (痰湿阻滞证)
Overconsumption of oily, fried and spicy food in our humid weather puts pressure on our digestive system. As more resources are used in the digestion of such food, pathogenic factors like Dampness can build up easily. This eventually leads to Phlegm-Damp syndrome in the TCM perspective.
Phlegm-Damp syndrome occurs when Dampness accumulates in the body, resulting in a buildup of pathogenic Phlegm that remains in the lower pelvic region. The buildup of Phlegm in the lower pelvic region blocks and impedes the Qi flowing into and out of the sexual organs during intercourse, causing erectile dysfunction, decreased libido and eventually sexual anxiety.
4. Yin deficiency raging Fire syndrome (阴虚火旺证)
Late nights, all-nighters and over-consumption of caffeine leads to over-activation of our sympathetic nervous system. This causes our “fight or flight” response to be turned on. When this response does not turn off, it leads to what is known in TCM as Yin deficiency raging Fire syndrome.
Typically, a healthy individual would be able to self-regulate and turn it off but when this fails to occur, we experience heart palpitations, night sweats, strong thirst and irritability that is associated with this syndrome.
When Yin is deficient, Blood will be weak. This leads to poor circulation in the body thus leading to erectile dysfunction. In addition, when Yin is deficient, Yang is relatively in abundance. This causes Heat to build up, causing over-stimulation and leading to premature ejaculation.
5. Heart-Spleen deficiency syndrome (心脾两虚证)
In TCM, each of our Five Organs resonates with one of the five different emotional states – the Heart governs joy/hate; Spleen governs trust/worry and anxiety.
According to the 5 elements theory, the Heart is the mother of the Spleen. This is because Fire (Heart’s element) produces Earth (Spleen’s element) according to their elemental relationships.
When things don’t go our way, it can stir up emotions like hate or worry which resonate with our Heart and Spleen. As the 2 organs are closely related, such emotions can affect the Spleen’s function in the formation of Blood, leading to poor appetite, weak muscles and poor circulation. This affects erectile function, libido and causes premature ejaculation.
6. Blood-stasis syndrome (血脉瘀滞证)
According to TCM, prolonged illness can affect the vessels and injure the Blood (久则血伤入络). This occurs because Qi and Blood share a mutual relationship and are thought to support one another in their function. Furthermore, Qi is the driver of Blood (气能行血). Without the function of Qi, Blood would not circulate.
The body pools its resources into fighting off the pathogen in prolonged illness, Qi is used for other purposes instead of moving the Blood. Over a long period of time, this can eventually affect erectile functions.
Getting treatment for male sexual dysfunction

Step 1: Identifying your problem and finding the root cause
Western doctors and TCM physicians typically assess the severity of your issue with the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) survey, Premature Ejaculation Diagnostic Tool (PEDT) survey and Intravaginal Ejaculation Latency Time (IELT) survey. These surveys are usually self-directed assessments – read more about how you can do a self-assessment here.
In addition, TCM physicians will also examine your body condition with diagnostic practices like pulse taking, tongue examination and an in-depth inquiry on your lifestyle (sleep, appetite, bowel and urinary habits) and medical history. In some cases, your doctor/physician may want to perform a physical examination, order blood tests and even explore your psychological history.
If you already have blood work done or have done blood testosterone and prolactin level test, bring your results to the consultation. Your doctor or physician will also check if you have tried other treatments or made changes to your lifestyle prior to the consultation.
In this day and age of technology, teleconsults are available if you prefer a more discreet way of seeking medical help. SIRE is a trusted men’s health virtual clinic solely for men in Singapore – book a teleconsult with a western doctor here.
Step 2: Western and TCM treatments for male sexual dysfunction
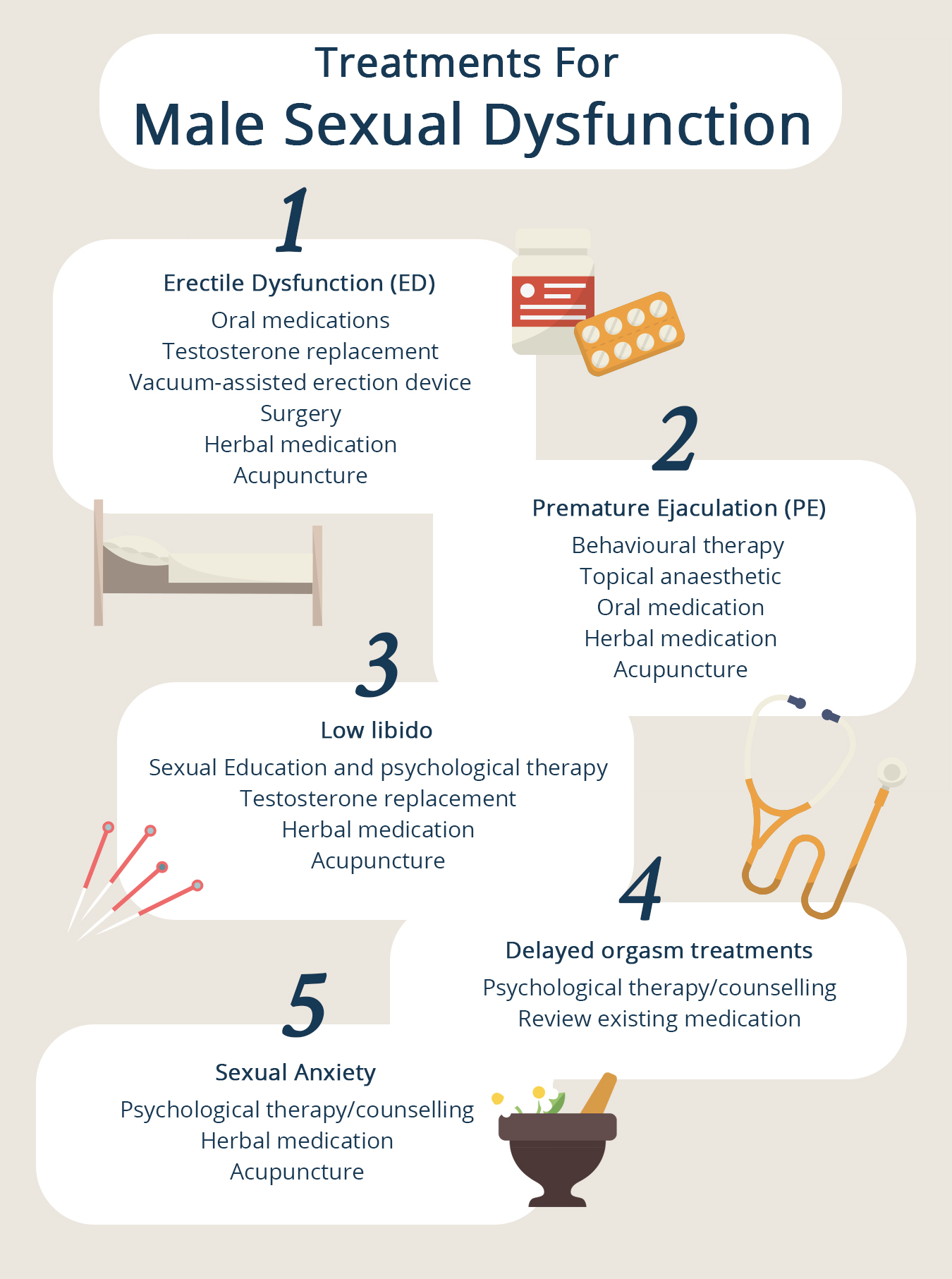
Both western and TCM treatments focus on the underlying causes of sexual dysfunction to cater to a treatment plan. In TCM, sexual dysfunction treatments generally seek to restore balance and harmony in the body through herbal medication, acupuncture, dietary and lifestyle changes.
|
Western and TCM treatments for male sexual dysfunction |
|
| Erectile Dysfunction (ED) | Oral medications Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitors (e.g. sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil, avanafil) are commonly prescribed.
Testosterone replacement
Vacuum-assisted erection device
Surgery
Herbal medication
Acupuncture
|
| Premature Ejaculation (PE) | Behavioural
Topical anaesthetic
Oral medication
Herbal medication
Acupuncture
|
| Low libido | Sexual Education and psychological therapy
Testosterone replacement Herbal medication
Acupuncture
|
| Delayed orgasm treatments | Psychological therapy/counselling
Review existing medication |
| Sexual Anxiety | Psychological therapy/counselling
Herbal medication
Acupuncture
|
Can you combine western and TCM treatments?
Yes, you can use western and TCM treatments concurrently to manage and improve sexual dysfunction. TCM has been a complementary treatment alongside western treatments for a long time. However, it is important to note that some herbs in TCM prescriptions might have an effect on western oral medications (i.e., increase/decrease the medication concentration in your body, increase the likelihood of certain side effects). Thus, it is always advisable to consult a trusted doctor and professional physician when you are looking to complement both western and TCM approaches to work on the issues collaboratively.
Other TCM treatments, e.g. Acupuncture, Cell Pro Therapy (CPT) or Electro-Lymphatic Therapy (ELT) generally do not interfere with western treatments.
Top tips to alleviate sexual dysfunction in men
|
Lifestyle Habits |
|
|
|
| Diet | |
|
|
| Mental and emotional health | |
|
This article is co-written by Senior Physician Lim Jing Yang from Oriental Remedies Group and Dr. Chan Jun Yang from SIRE, a trusted men’s health virtual clinic solely for Men in Singapore.
Senior Physician Lim has worked with numerous patients suffering from male sexual dysfunction in both Singapore and China. By combining Traditional Chinese Medicine therapies and expertise with modern integrative therapies, we strive to provide the best care possible in your journey with us. If you are looking to manage male sexual dysfunction with TCM, please contact us at +65 8087 0486 for a personalized consultation.


|
Sire is powered by The Cloud Clinic, a Ministry of Health registered telemedicine clinic. Learn more about LICENSING TELEMEDICINE SERVICE UNDER HCSA Cloud Clinic is a Singapore healthcare institution focused on providing direct-to-home healthcare solutions. Every product and service we provide is specially curated and supervised by our medical team. |
Note: All words in Italics refer to the TCM organ-system and not the anatomical organ referenced in western medicine.
Disclaimer:
The information on this page is for information and educational purposes only. Such medical information may relate to disease, injury, drugs and other treatments, medical devices and/or health products. Medical information does not amount to advice, and if advice is needed an appropriate professional help should be sought. The disclaimer asserts that no warranties or representations are given in respect of the medical information, and that the website operator should not be held liable if a user suffers any injury or loss after relying upon the medical information.
All wellness assessments and technology-enhanced therapies using wellness device(s) are intended for use only for general well-being purposes or to encourage or maintain a healthy lifestyle, and it is not intended to be used for any medical purposes (such as detection, diagnosis, monitoring, management or treatment of any medical condition or disease). Any health-related information provided by these devices should not be treated as a medical advice. Please consult a physician for any medical advice required.
Additional References:
1. Epidemiology and etiologies of male sexual dysfunction. UpToDate.
2. Kaminetsky, J. Epidemiology and pathophysiology of male sexual dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 20, S3–S10 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2008.16
3. Loss of libido (reduced sex drive). https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/loss-of-libido/
4. Jenkins LC, Mulhall JP. Delayed orgasm and anorgasmia. Fertil Steril. 2015;104(5):1082-1088. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.09.029
5. Ejaculatory problems. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/ejaculation-problems/
6. Evaluation of male sexual dysfunction. UpToDate.
7. Treatment of male sexual dysfunction. UpToDate.
8. International Society for Sexual Medicine (ISSM). What is delayed ejaculation? https://www.issm.info/sexual-health-qa/what-is-delayed-ejaculation/
9. International Society for Sexual Medicine (ISSM). Premature Ejaculation guidelines.
10. Foods to eat for better sex. Medical News Today. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/322779
11. West E, Krychman M. Natural Aphrodisiacs-A Review of Selected Sexual Enhancers. Sex Med Rev. 2015;3(4):279-288. doi:10.1002/smrj.62